Workshop 03: Rate law and stoichiometry
Lecture notes for chemical reaction engineering
Solutions to these problems are uploaded at Workshop 3 solutions
Try following problems from Fogler 5e(Fogler 2016).
P3-5, P3-10, P3-11, P3-12, P 4-6, P 4-8, P 4-11
We will go through some of these problems in the workshop.
P 3.12
Write the rate law for the following reactions assuming each reaction follows an elementary rate law. Give the units of for each, keeping in mind some are homogeneous and some reactants are heterogeneous.
P3-10
The initial reaction rate for the elementary reaction was measured as a function of temperature when the concentration of A was 2 M and that of B was 1.5 M.
| 0.002 | 300 |
| 0.046 | 320 |
| 0.72 | 340 |
| 8.33 | 360 |
What is the activation energy?
What is the frequency factor?
What is the rate constant as a function of temperature using Equation 1 and = 27 °C as the base case?
P 4-8
The gas-phase reaction
is to be carried out isothermally first in a flow reactor. The molar feed is 50% and 50% , at a pressure of 16.4 atm and at a temperature of ?.
Construct a complete stoichiometric table.
Express the concentrations in of each for the reacting species as a function of conversion. Evaluate , and , and then calculate the concentrations of ammonia and hydrogen when the conversion of is 60%.
Suppose by chance the reaction is elementary with . Write the rate of reaction solely as a function of conversion for
a flow reactor, and for
a constant-volume batch reactor.
P 4-11
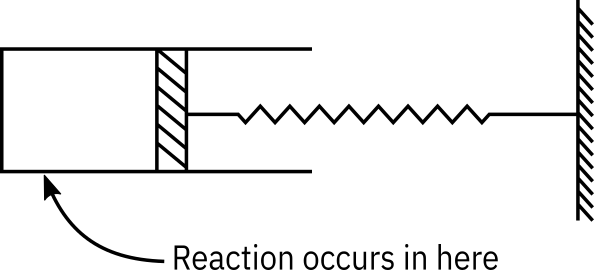
Consider a cylindrical batch reactor that has one end fitted with a frictionless piston attached to a spring (See Figure Figure 1). The reaction
with the rate law
is taking place in this type of reactor.
Write the rate law solely as a function of conversion, numerically evaluating all possible symbols.
What is the conversion and rate of reaction when ?
Additional information:
Equal moles of A and B are present at
Initial volume:
Value of
The spring constant is such that the relationship between the volume of the reactor and pressure within the reactor is
(V in , P in )
Temperature of system (considered constant):
Gas constant:
References
Citation
@online{utikar2024,
author = {Utikar, Ranjeet},
title = {Workshop 03: {Rate} Law and Stoichiometry},
date = {2024-03-10},
url = {https://cre.smilelab.dev/content/workshops/03-rate-law-and-stoichiometry/},
langid = {en}
}