import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from scipy.integrate import solve_ivp
# constants
RCAL = 1.987 # cal⋅/ mol K
# data
NU_VIS = 0.02 # cm^2/s
DP = 0.1 # cm
VEL = 10 # cm/s
SP_AREA = 60 # cm^2/g-cat
DE = 1e-2 # cm^2/s
DELTA_HR_TR = 10000 # cal/gmol A
CPA = 25 # cal/gmol K
CPB = 25 # cal/gmol K
CPS = 75 # cal/gmol K -- Solvent is inert
KA0 = 0.01 # cm^3/s g-cat
EA0 = 4000 # cal/mol
TR = 300 # K
# Functions
k = lambda t: KA0 * np.exp((EA0 / RCAL) * ((1 / TR) - (1 / t)))
def reactor(w, y, *args):
# convert dependent variables
x = y[0]
(t0, ca0, fa0, phia, phis, kc) = args
# isothermal case
t = t0
# Adiabatic case
t = t0 + (x * DELTA_HR_TR / (phia * CPA + phis * CPS))
ca = ca0 * (1-x) * (t0/t)
rate = k(t) * kc * ca / (k(t) + kc)
dxdw = rate / fa0
dydw = [dxdw]
return dydw
# Problem data
ca0 = 1.0e-3 # mol/cm^3
v0 = 1.0e4 # cm^3/s
t0 = 300
phia = 1 # 50% A in inlet
phis = 1 # 50% A in inlet
Re = DP * VEL/ NU_VIS
Sh = 100 * Re**0.5
kc = Sh * DE/DP # cm/s
kc = kc * SP_AREA # cm^3 /s g-cat
fa0 = ca0 * v0
args = (t0, ca0, fa0, phia, phis, kc)
initial_conditions = np.array([0])
w_final = 1e6 # 1000 kg
sol = solve_ivp(
reactor,
[0, w_final],
initial_conditions,
args=args,
method="LSODA",
dense_output=True,
)
# Extract solution
w = np.linspace(0, w_final, 1000)
# conversion
x = sol.sol(w)[0]
# isothermal case
t = np.full(len(w), t0)
# adiabatic case
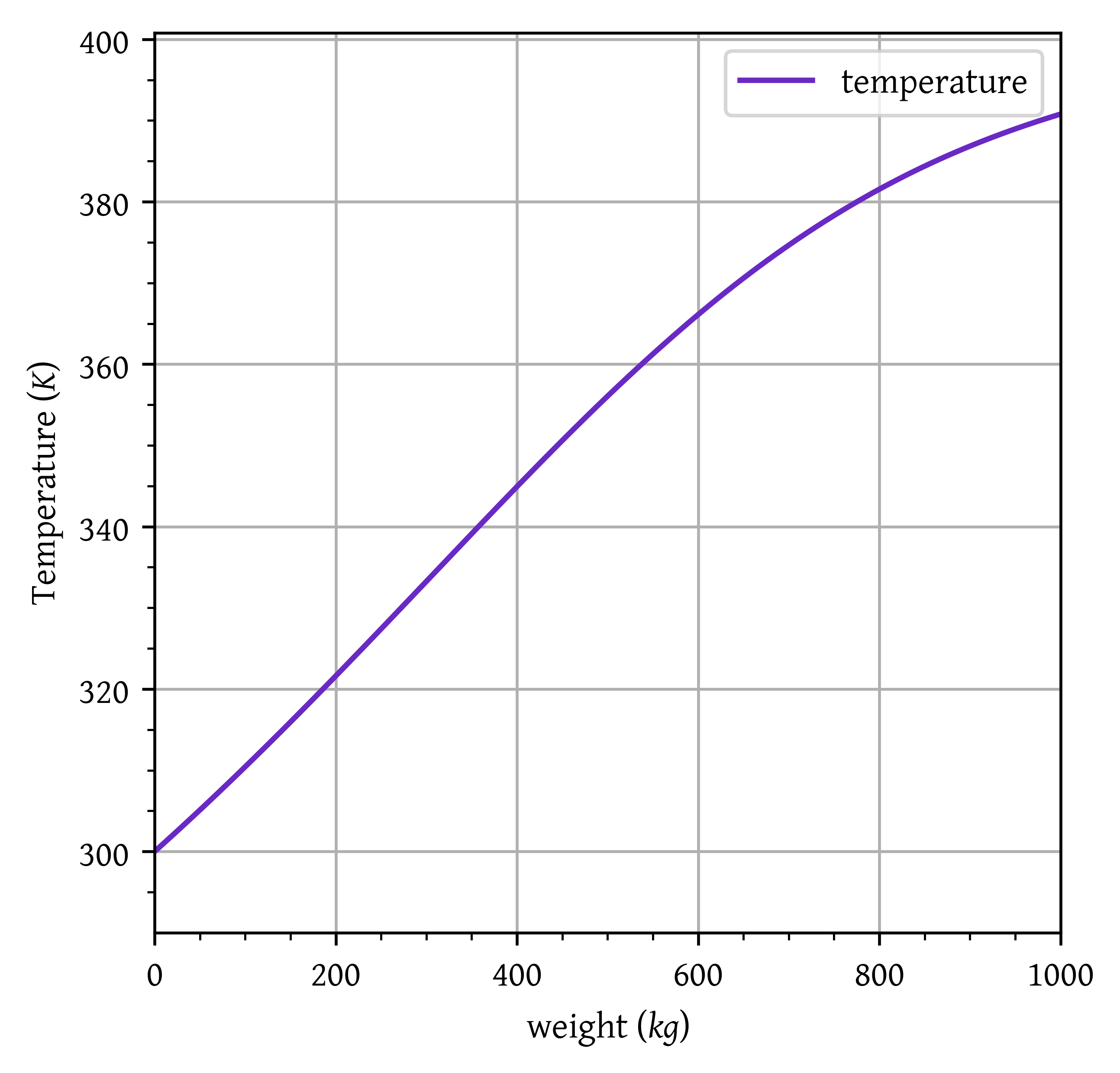
t = t0 + (x * DELTA_HR_TR / (phia * CPA + phis * CPS))Solutions to workshop 09: External diffusion effects
Lecture notes for chemical reaction engineering
P 14-9
The irreversible gas-phase reaction
is carried out adiabatically over a packed bed of solid catalyst particles. The reaction is first order in the concentration of A on the catalyst surface
The feed consists of 50% (mole) A and 50% inerts, and enters the bed at a temperature of 300 K. The entering volumetric flow rate is 10 dm3/s (i.e., 10,000 cm3/s). The relationship between the Sherwood number and the Reynolds number is
As a first approximation, one may neglect pressure drop. The entering concentration of A is 1.0 M. Calculate the catalyst weight necessary to achieve 60% conversion of A for
isothermal operation.
adiabatic operation.
Additional information:
- Kinematic viscosity:
- Particle diameter:
- Superficial velocity:
- Catalyst surface area/mass of catalyst bed:
- Diffusivity of A:
- Heat of reaction:
- Heat capacities:
= 4242.641
= 0.001
= 10.000
= 300.000 K
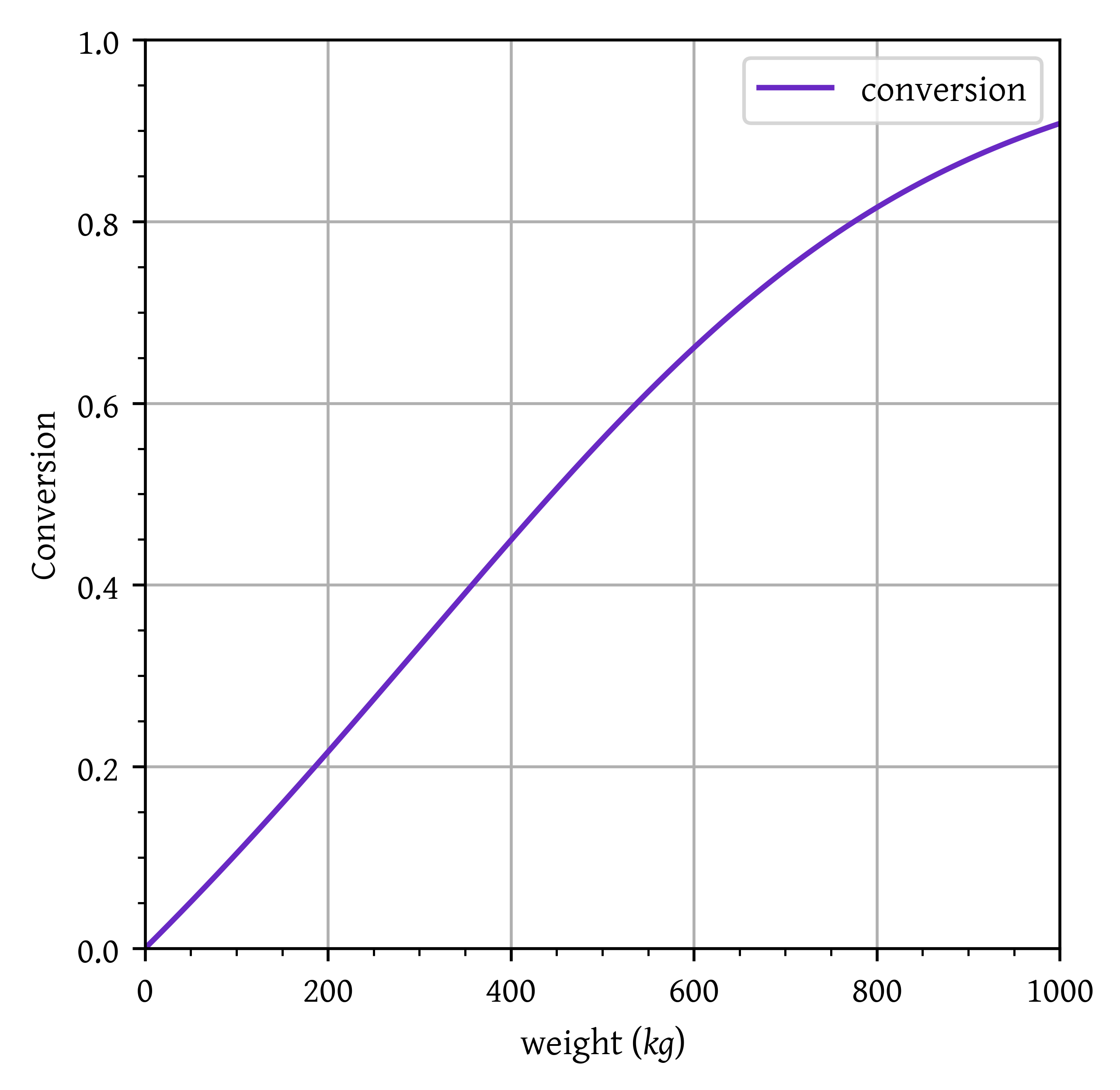
Catalyst weight required for X = 0.6: 538.539 kg
Temperature: 360.08 K
plt.plot(w/1000, x, label="conversion")
plt.xlim(w[0]/1000, w[-1]/1000)
plt.ylim(0, 1)
plt.grid()
plt.legend()
plt.xlabel("weight ($kg$)")
plt.ylabel("Conversion")
plt.show()Citation
@online{utikar2024,
author = {Utikar, Ranjeet},
title = {Solutions to Workshop 09: {External} Diffusion Effects},
date = {2024-03-24},
url = {https://cre.smilelab.dev/content/workshops/09-external-and-internal-diffusion-effects/solutions.html},
langid = {en}
}